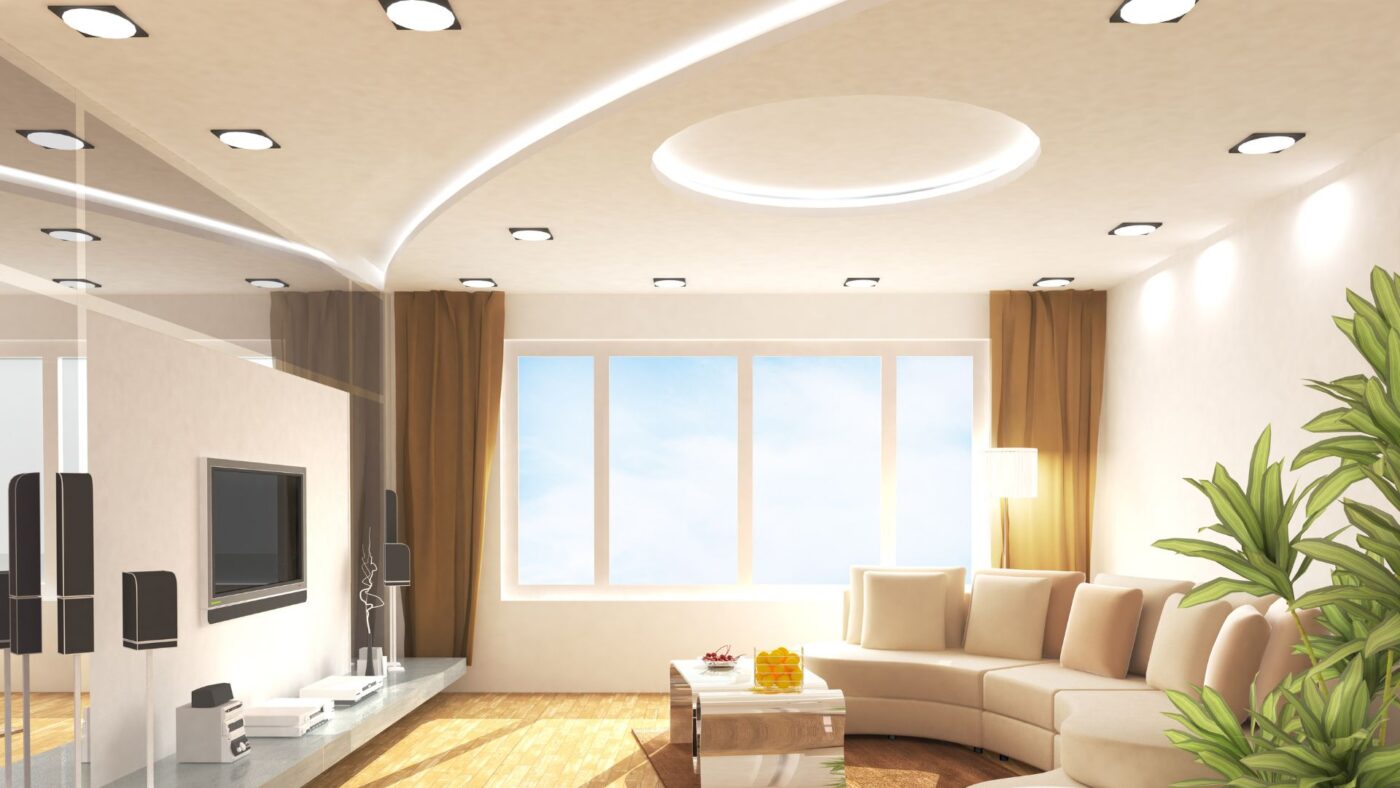
A suspended ceiling, also known as a drop ceiling, is a secondary ceiling that is hung below the original ceiling using a grid system of metal channels. The suspended ceiling is typically made up of a series of ceiling tiles that are inserted into the grid, creating a new, lower ceiling.
The suspended ceiling grid system consists of a series of metal channels, known as main runners, that are suspended from the original ceiling using wires or other supports. The main runners are typically installed in a grid pattern that corresponds to the size and shape of the ceiling tiles.
Cross runners, also known as T-bars, are installed perpendicular to the main runners, creating a grid pattern that supports the ceiling tiles. The cross runners are inserted into slots in the main runners, creating a secure and stable support system for the ceiling tiles.
Ceiling tiles are then inserted into the grid system, making sure that they are properly aligned and secured. The tiles are typically made from a variety of materials, including mineral fiber, fiberglass, PVC, or metal.
If lighting fixtures are desired, holes can be cut in the ceiling tiles to accommodate the fixtures. Wiring for the fixtures is then installed, typically by running electrical wires through the grid system and connecting them to the fixtures.
In addition to providing a new, lowered ceiling, suspended ceilings offer a variety of benefits, including improved acoustics, better thermal insulation, and easy access to the space above the ceiling for maintenance and repairs.
Overall, a suspended ceiling is a versatile and functional option for improving the appearance and functionality of a space. With many different materials, finishes, and design options available, suspended ceilings can be customized to fit a wide range of needs and preferences.

 Русский
Русский العربية
العربية Français
Français Türkçe
Türkçe Română
Română Português
Português ქართული
ქართული български
български Magyar
Magyar